IPv6 book with MikroTik, RouterOS v7
Study material for the MTCIPv6E Certification Course updated to RouterOS v7
In IPv6, the extension headers are additional data structures that are inserted between the IPv6 header and the upper layer protocol header (such as TCP or UDP) in an IPv6 packet.
These extension headers provide additional functionality and allow greater flexibility in processing IPv6 packets. Unlike IPv4, where options were included directly in the IP header, IPv6 uses separate extension headers to include additional information.
At the end of the article you will find a small test that will allow you assess the knowledge acquired in this reading
In an IPv6 packet, the main header consists of 40 bytes Fixed fields that include source address, destination address, traffic type, and other fields necessary for routing and package delivery. After the main header, one or more extension headers may follow, depending on the specific needs of the communication.
Extension headers in IPv6 are identified by a field called “Next Header” (Next Header) in the IPv6 header. Field “Next Header” specifies the type of the next header, which can be a higher layer protocol or an extension header. When an extension header is present, the “Next Header” field points to the extension header type and subsequent extension headers follow it.
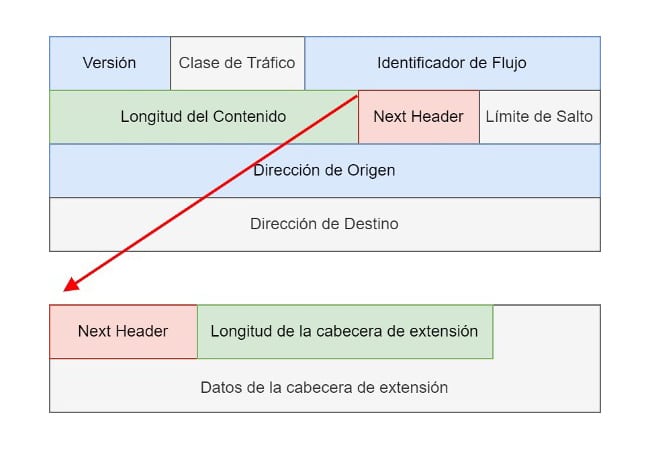
Each extension header is made up of two main parts:
It is a data structure that contains information about the type of extension header and its length in units of 8 bytes (64 bits). The extension header includes the Next Header type, which indicates whether the next header is another extension header or the upper layer protocol header.
It is the part of the extension header that carries the additional data specific to that header. The format and content of the extension body varies depending on the type of extension header. For example, the Hop-by-Hop Options header may carry additional options that must be examined by all nodes along the packet delivery path.
Extension headers in IPv6 allow greater modularity and flexibility in protocol design. Additionally, by separating additional options and functionality into extension headers, unnecessary processing of options by nodes that do not require them is avoided.
It is important to note that not all extension headers are required in all IPv6 packets. The inclusion and order of extension headers depends on the specific requirements and characteristics of the communication. Some extension headers are used only in particular cases, such as packet fragmentation, authentication, or mobility.
Extension headers are identified by a different value:
Extension Headers | Market |
Hop-by-Hop | 0 |
Fragment | 44 |
Routing (Type) | 43 |
Destination Options | 60 |
Authentication | 51 |
Encapsulating Security Payload | 50 |
This header is used for options that must be examined by each node along the packet delivery path, this being mandatory. It can carry various options such as multicast listener discovery, packet filtering or quality of service (QoS) information.
Hop by Hop options may include:
Used to pad the hop-by-hop options header to ensure its length is a multiple of 8 bytes.
Allows routers to perform special actions on the packet. For example, it can be used to notify routers that the packet must be treated with priority or that it requires special treatment.
This option is used to indicate that the packet contains a payload greater than the maximum transmission size (MTU) of a link. It is used for the transmission of IPv6 packets with payload sizes larger than the standard MTU.
Hop by Hop options header processing involves each node along the packet delivery path examining and processing the relevant options. Each node must complete the actions specified in the step-by-step options before continuing to process the packet. This allows options to be used for specific functions in the network, such as flow control, packet prioritization, or enabling special services.
It is important to note that using the hop-by-hop options header can have an impact on network performance as it requires additional processing at each node along the path. Therefore, it is recommended to use hop-by-hop options only when necessary and justified by application or network requirements.
The Routing extension header in IPv6 is used to allow IPv6 packets to be routed through a specific series of nodes on the network. The Routing extension header can appear in an IPv6 packet after the Hop-by-Hop extension header or after any other extension header.
The Routing extension header is used to establish an explicit route through which an IPv6 packet must pass. The Segments Left field is decremented by one at each node the packet visits along the route. When the Segments Left value reaches zero, the packet has reached its final destination.
The Routing extension header in IPv6 is used in specific situations where explicit control over the path a packet should follow on the network is required.
By specifying the route in the Routing extension header, you can achieve precise routing and prevent packets from following the default routes determined by the routers' routing tables.
Here are some cases where you can use the Routing extension header:
On some networks, you may want to apply specific routing policies for certain types of traffic. The Routing extension header allows you to specify a custom route that meets the requirements of the established routing policy. This may include routing through specific nodes or avoiding certain network links.
At times, traffic may be required to be routed through nodes in specific geographic locations. The Routing extension header allows you to specify a route that includes the desired nodes in the required geographic location.
In some cases, it may be necessary to avoid specific nodes or links due to performance issues, security, or other considerations. The Routing extension header can be used to specify a route that avoids unwanted nodes or links.
In situations where low latency or high bandwidth is required for traffic, the Routing extension header can be used to specify a route that guarantees these requirements. This may include routing over high-capacity or low-latency nodes or links.
It is important to note that the use of the Routing extension header in IPv6 is not as common as the use of other types of extension headers. In most cases, routing in IPv6 is based on the routers' routing table, which determines the best route for the packet based on the destination address and other routing policies.
The extension header Destination Options (destination options) in IPv6 is used to provide additional options related to the final destination of the IPv6 packet. This header is placed after the IPv6 extension header and before the payload header.
The Destination Options extension header allows IPv6 packets to carry additional information related to the final destination, providing greater flexibility and functionality.
By including options in the Destination Options extension header, additional features can be added to IPv6 packets based on specific application or protocol needs.
It is necessary to take into consideration that the options in the Destination Options extension header are processed by the receiving nodes according to their type. If a receiving node is unable to process a specific option, it can ignore or discard it. Options that cannot be processed do not affect basic IPv6 packet forwarding or routing.
The Destination Options extension header is used in several scenarios to provide additional options related to the final destination of the packet. Below are some cases where the extension header can be used Destination Options:
The Destination Options extension header can be used to include options related to security and authentication. This may include public key information for end-to-end authentication, or digital signatures to verify the integrity of the packet data.
In some cases, you may want to specify quality of service requirements for an IPv6 packet. This header may include options that indicate requirements for bandwidth, delay, packet loss, or other QoS parameters.
In situations where specific routing is required for an IPv6 packet, you can include options that specify the route or nodes to visit. This allows greater control over the routing path and the ability to avoid certain links or network nodes.
The header can be used to indicate special actions that must be performed on the receiving nodes. For example, it may include options to perform specific manipulations on the packet payload or to perform additional processing operations on the receiving node.
Study material for the MTCIPv6E Certification Course updated to RouterOS v7
Av. Juan T. Marengo and J. Orrantia
Professional Center Building, Office 507
Guayaquil. Ecuador
Zip Code 090505
to our weekly newsletters
Copyright © 2024 abcxperts.com – All Rights Reserved
40% discount on MikroTik books and book packs - Discount Code: AN24-LIB Discard
Take advantage of the Three Kings Day discount code!
Take advantage of the New Year's Eve discount code!
Take advantage of the discount code for Christmas!!!
all MikroTik OnLine courses
all Academy courses
all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
Take advantage of the discount codes for Cyber Week!!!
all MikroTik OnLine courses
all Academy courses
all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
Take advantage of the discount codes for Black Friday!!!
**Codes are applied in the shopping cart
Take advantage of discount codes for Halloween.
Codes are applied in the shopping cart
11% discount on all MikroTik OnLine courses
11%
30% discount on all Academy courses
30%
25% discount on all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
25%