IPv6 book with MikroTik, RouterOS v7
Study material for the MTCIPv6E Certification Course updated to RouterOS v7
The directions IPv6 unicast They have a further subdivision into specific categories and are as follows:
At the end of the article you will find a small test that will allow you assess the knowledge acquired in this reading
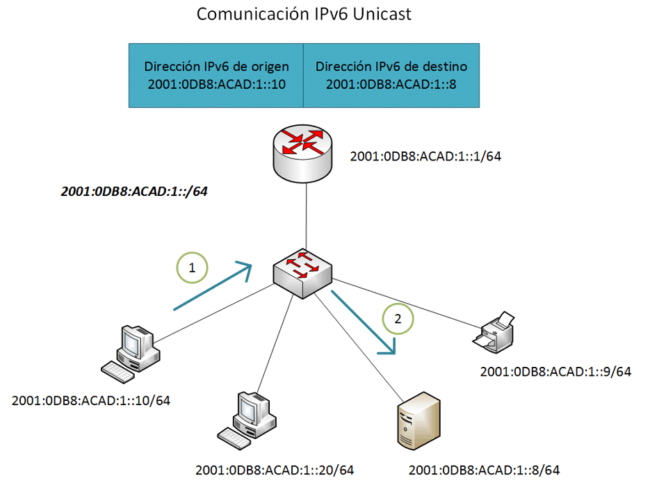
IPv6 global unicast addresses (GUAs) are a type of IPv6 unicast address used to uniquely identify a network interface on the Internet.
These addresses are assigned and registered by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) to organizations and Internet service providers.
Below is a more detailed explanation of global unicast IPv6 addresses:
IPv6 global unicast addresses have a 128-bit structure and are represented in hexadecimal notation. They are divided into eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by a colon (:). For example: 2001:0db8:0123:4567::1.
GUA addresses are characterized by having a global prefix that indicates that they are unique addresses on the Internet. These prefixes are assigned by IANA to Regional Internet Registries (RIRs), such as ARIN, RIPE NCC, APNIC, LACNIC and AfriNIC, who in turn assign them to organizations and Internet service providers in their respective regions.
Each global unicast IPv6 address is unique and should not be repeated on the Internet. This means that each network interface on the Internet must have a unique GUA address to ensure connectivity and accurate identification on the network.
IPv6 global unicast addresses are used to route packets over the Internet. Internet routers use the global prefix information to determine the proper route and send packets to the correct destination on the global network.
GUA addresses allow point-to-point communication over the Internet. Devices with a GUA address can establish direct connections and send packets to other devices that also have GUA addresses.
Global unicast IPv6 address allocation is accomplished by requesting address blocks from RIRs. Organizations and Internet service providers request blocks of IPv6 addresses from RIRs based on their needs and the size of the network they want to deploy.
IPv6 global unicast addresses are used in a wide variety of services and applications on the Internet, such as web browsing, email, cloud services, video conferencing, data transmission, and many other IP-based applications.
In summary, IPv6 global unicast addresses are used to uniquely identify network interfaces on the Internet. They are assigned by the IANA to organizations and Internet service providers and are used for communication and routing on the global network. These addresses are essential for the connectivity and functioning of the Internet as a whole.
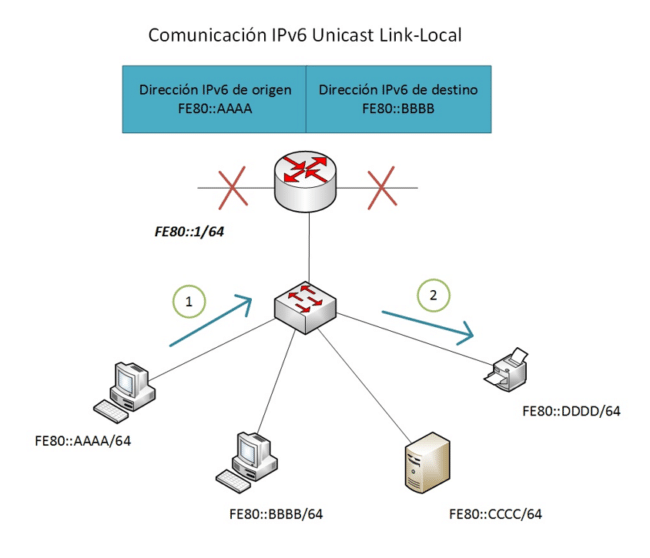
IPv6 unicast link-local addresses are a type of IPv6 address used for communication on a specific network link or segment. These addresses are valid only within the link and are not routed beyond it.
Below is a detailed explanation of IPv6 unicast link-local addresses:
IPv6 unicast link-local addresses are designed to allow communication on a local link without the need for a router. These addresses are used for automatic address configuration, neighbor resolution, and other neighbor discovery services within the link.
IPv6 unicast link-local addresses have a specific prefix, which is “fe80::/10”. The initial 10 bits of the prefix are always set to “1111111010”, which is represented as “fe8” in hexadecimal notation. The remaining 54 bits are available for interface identification on the local link.
IPv6 unicast link-local addresses are automatically configured on network interfaces without the need for a configuration server. This is achieved through IPv6's stateless autoconfiguration process, where an interface assigns a link-local address to itself without manual intervention.
IPv6 unicast link-local addresses are not routed outside the link-local. This means that packets sent to a link-local address are only delivered to interfaces within the same link and are not propagated through routers on the Internet.
On a local network, it is important to ensure that IPv6 unicast link-local addresses are unique on each network interface. If two interfaces on the same link have the same link-local address, a collision occurs and there may be communication problems. To avoid this, the IPv6 address conflict resolution process is used, where interfaces check whether a link-local address is being used before assigning it to themselves.
IPv6 unicast link-local addresses are used in various aspects of network configuration and operation. Some examples include:
Link-local addresses are used to assign addresses to network interfaces on a link-local during autoconfiguration.
Link-local addresses are used for discovery and resolution of neighbors on a local link. IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) uses link-local addresses to resolve neighbor MAC addresses and establish communication on the link.
Some internal protocols and services use link-local addresses to advertise their availability on the local link, allowing other devices to discover and use those services.
Link-local addresses are useful in diagnosing and troubleshooting network problems because they allow direct communication between devices on the same link without the need for routing.
IPv6 unicast link-local addresses are essential for the operation and configuration of local networks in IPv6. They provide a unique way to identify and communicate with network interfaces on the same link, facilitating neighbor discovery and other internal network services.
IPv6 loopback addresses are special addresses used for testing and local communication on a device without packets being sent over the network. These addresses allow a device to communicate with itself without needing to go through a physical network interface.
As with IPv4 loopback addresses, IPv6 loopback addresses have some important characteristics:
Here's more information about IPv6 loopback addresses:
The standard IPv6 loopback address is “::1” or simply “::1/128”. It is equivalent to the IPv4 loopback address “127.0.0.1”. This address is reserved specifically for loopback use and is present on all devices with IPv6 support.
When a device sends a packet to the loopback address “::1”, the packet is delivered directly to the device itself without going out to the network. This allows applications and services to communicate with themselves without needing a physical network interface or affecting other devices on the network.
Applications and services can take advantage of the IPv6 loopback address for various purposes:
Applications can send and receive data over the IPv6 loopback address for testing and verification of proper operation without relying on an external network connection.
Developers can use the IPv6 loopback address to test and debug applications before deploying them in a real network environment.
By emulating services on the IPv6 loopback address, you can test the interaction of different components of a system without affecting the external network.
Diagnostic and monitoring tools can use the IPv6 loopback address to evaluate the health of the network stack and detect potential problems without affecting external connectivity.
Study material for the MTCIPv6E Certification Course updated to RouterOS v7
Av. Juan T. Marengo and J. Orrantia
Professional Center Building, Office 507
Guayaquil. Ecuador
Zip Code 090505
to our weekly newsletters
Copyright © 2024 abcxperts.com – All Rights Reserved
40% discount on MikroTik books and book packs - Discount Code: AN24-LIB Discard
Take advantage of the Three Kings Day discount code!
Take advantage of the New Year's Eve discount code!
Take advantage of the discount code for Christmas!!!
all MikroTik OnLine courses
all Academy courses
all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
Take advantage of the discount codes for Cyber Week!!!
all MikroTik OnLine courses
all Academy courses
all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
Take advantage of the discount codes for Black Friday!!!
**Codes are applied in the shopping cart
Take advantage of discount codes for Halloween.
Codes are applied in the shopping cart
11% discount on all MikroTik OnLine courses
11%
30% discount on all Academy courses
30%
25% discount on all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
25%