IPv6 book with MikroTik, RouterOS v7
Study material for the MTCIPv6E Certification Course updated to RouterOS v7
Like IPv4 addressing, IPv6 addresses are also classified into different types based on their configuration.
At the end of the article you will find a small test that will allow you assess the knowledge acquired in this reading
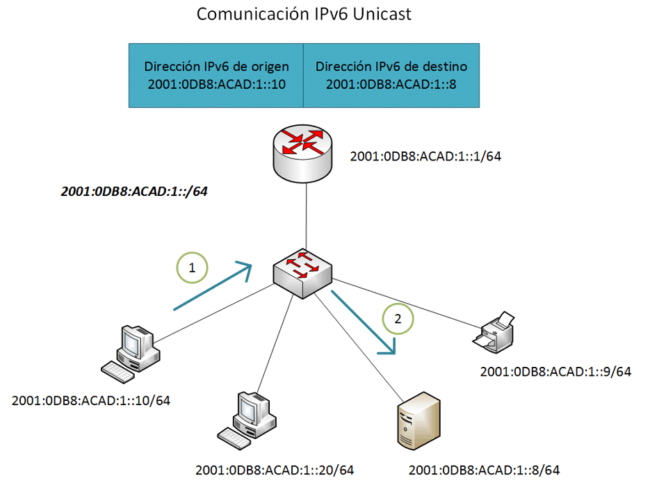
IPv6 unicast addresses are addresses that are assigned to individual interfaces on a network and are used for point-to-point communication. These addresses uniquely identify a network interface and allow packets to be delivered directly to that interface.
Below, we'll delve into some key aspects of IPv6 unicast addresses:
IPv6 unicast addresses are made up of 128 bits and are represented in hexadecimal notation. They are divided into eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by a colon (:).
Por ejemplo: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334.
IPv6 unicast addresses allow point-to-point communication between devices on a network. They are used to establish direct connections and send packets from a source to a specific destination.
These addresses are essential for the functioning of the Internet and are used by a wide variety of applications and services, such as web browsing, email, data transmission, video conferencing, among others.
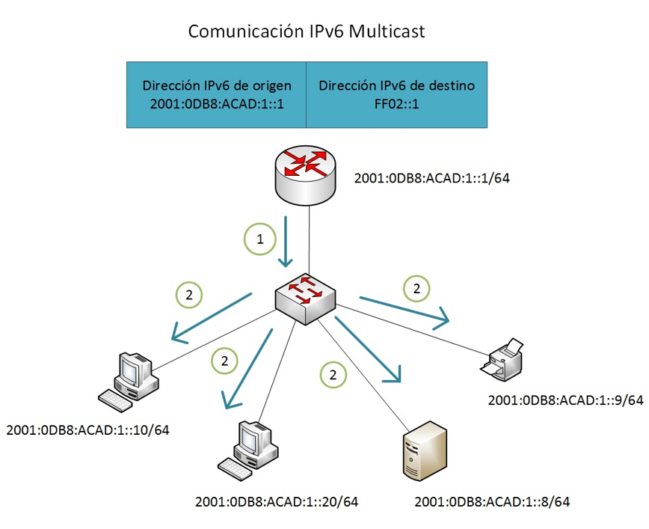
IPv6 multicast addresses are a type of address used for one-to-many communication on IPv6 networks. Unlike unicast addresses that are used for one-to-one communication, multicast addresses allow packets to be delivered to multiple recipients efficiently. Below is a detailed explanation about IPv6 multicast addresses
IPv6 multicast addresses are defined in the address range “ff00::/8”. These addresses are divided into two parts:
Well-known IPv6 multicast addresses are predefined, reserved multicast addresses that are commonly used for specific applications and services. These multicast addresses have a predefined meaning and are assigned for use in particular scenarios. There are some well-known multicast addresses reserved for specific uses in IPv6, such as:
This address is used to send traffic to all nodes on a local network. Devices can join this address to receive announcements and messages sent to all nodes. It is used, for example, for neighbor discovery and address resolution on the local network.
This address is used to send traffic to all routers on a local network. Devices can join this address to receive announcements and messages sent to all routers. It is used, for example, for router discovery and automatic IPv6 address configuration.
This address is used to send name resolution queries to all DNS servers on a network. Devices can bind to this address to receive responses from all available DNS servers on the network.
This address is used to send OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) routing-related traffic to all routers running OSPF on a network. It is used for exchanging OSPF routing information and maintaining network topology.
This address is used to send Routing Information Protocol (RIP)-related traffic to all routers running RIP on a network. It is used for exchanging RIP routing information and maintaining the routing table.
These multicast addresses are automatically generated for each IPv6 unicast address and are used in the address resolution process using the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP). They are used to send address resolution requests to a specific node on the network.
Multicast addresses are used in various scenarios and applications, below we detail several:
Multicast addresses are used for the transmission of real-time multimedia content, such as live video, web conferencing, audio broadcasts, and content delivery on content delivery networks (CDN). This allows multiple users in different locations to access and view content simultaneously, reducing network load and optimizing bandwidth.
Multicast addresses are used in routing protocols to send routing updates to multiple routers within a network. They are also used in applications that require real-time coordination, such as online games, group collaboration, and instant messaging systems.
In Internet of Things (IoT) and sensor network environments, multicast addresses are used for communication between sensors, monitoring devices, and control systems. This allows efficient transmission of data and commands to multiple devices in real time.
Multicast addresses are also used in server and cluster replication environments for synchronization and communication between member servers. It allows servers in a cluster to share information and maintain synchronized state, improving availability and redundancy of services.
Multicast addresses are used in protocols such as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPv6) and Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) to facilitate the discovery and automatic configuration of devices on an IPv6 network. Devices can send multicast requests to obtain IP addresses or network configuration information.
IPv6 anycast addresses are a special type of address in IPv6 that is used to identify a group of devices that offer the same service or content in different geographic locations. Unlike unicast addresses, which are assigned to a single network interface, anycast addresses are assigned to multiple interfaces on different nodes in the network.
When a packet is sent to an anycast address, the network automatically determines the closest location and sends the packet to the nearest anycast node. This allows efficient distribution of traffic to the most suitable anycast node based on factors such as network latency or node load.
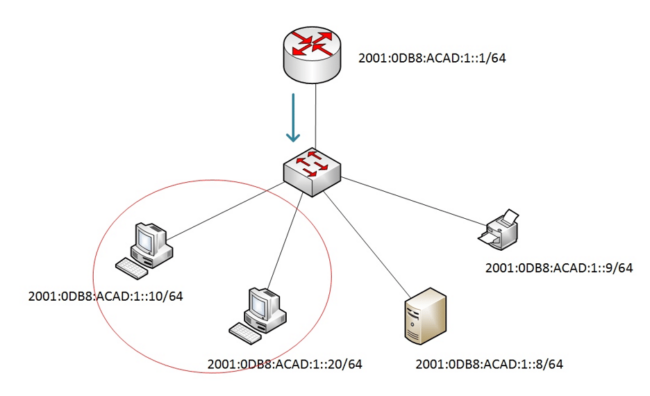
Below are the key aspects of IPv6 anycast addresses:
Anycast addresses are used to identify services or content that are available in multiple locations. Each node that offers the same service is assigned the same anycast address.
Routing of packets to anycast nodes is done through the network using existing routing protocols, such as OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) or BGP (Border Gateway Protocol).
Choosing the appropriate anycast node is based on the routing configuration and the metrics used by the routing protocols to select the best route.
The choice of the nearest anycast node is based on routing algorithms and network metrics.
Routers automatically determine the most efficient route to the nearest anycast node based on network topology and routing metrics.
The use of anycast addresses allows greater redundancy and availability in services. If one of the anycast nodes fails or becomes unreachable, the network redirects traffic to the next closest anycast node.
This ensures that the service is available even if some nodes fail.
IPv6 anycast addresses have several use cases in different network scenarios. Some of the common use cases for IPv6 anycast addresses are:
IPv6 anycast addresses are used in DNS servers to improve the availability and response speed of name resolution queries.
Multiple DNS servers in different geographic locations can advertise the same anycast address, and clients send their DNS queries to the closest location. This reduces latency and improves the user experience when accessing websites and other domain name-based services.
IPv6 anycast addresses are used in load balancing solutions to efficiently distribute traffic across multiple servers or clusters of servers.
Anycast servers advertise the same address, and routers direct client requests to the nearest anycast server based on network topology and routing metrics. This helps improve the performance, scalability, and availability of web and application services.
Anycast addresses are used in content delivery networks (CDNs) to distribute static and dynamic content across multiple servers in different geographic locations. Anycast servers advertise the same address, and clients are directed to the nearest anycast server to access content.
This reduces latency and improves content loading speed, especially for web applications and popular sites with a large amount of traffic.
Anycast addresses are used in time servers to provide accurate and reliable time synchronization services.
Multiple anycast servers advertise the same address, and clients get the response time of the nearest anycast server. This ensures that devices and systems on the network are synchronized and can function correctly over time.
Anycast addresses are used in routing protocols, such as OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and BGP (Border Gateway Protocol), to provide more efficient and scalable routing services. Multiple routers in different locations advertise the same anycast address to represent a common route to a specific destination.
This improves traffic distribution, redundancy, and network resiliency.
This chart only presents an overview of the differences between unicast, multicast, and anycast addresses.
unicast | Multicast | Anycast | |
Definition | Identifies a single network interface | Identify a group of recipients | Identifies a group of nodes |
Destination | A single receiver | Various receivers | The nearest anycast node |
Distribution | Point by point | one to many | One by one (closest node) |
Routing | Direct | Routed over the network | Routed over the network |
Addresses | Global unicast, link-local unicast, site-local unicast, etc. | Global multicast, link-local multicast, site-local multicast, etc. | Modified unicast (same address on different nodes) |
Study material for the MTCIPv6E Certification Course updated to RouterOS v7
Av. Juan T. Marengo and J. Orrantia
Professional Center Building, Office 507
Guayaquil. Ecuador
Zip Code 090505
to our weekly newsletters
Copyright © 2024 abcxperts.com – All Rights Reserved
40% discount on MikroTik books and book packs - Discount Code: AN24-LIB Discard
Take advantage of the Three Kings Day discount code!
Take advantage of the New Year's Eve discount code!
Take advantage of the discount code for Christmas!!!
all MikroTik OnLine courses
all Academy courses
all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
Take advantage of the discount codes for Cyber Week!!!
all MikroTik OnLine courses
all Academy courses
all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
Take advantage of the discount codes for Black Friday!!!
**Codes are applied in the shopping cart
Take advantage of discount codes for Halloween.
Codes are applied in the shopping cart
11% discount on all MikroTik OnLine courses
11%
30% discount on all Academy courses
30%
25% discount on all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
25%