(Book) Networking with MikroTik RouterOS: A Practical Approach to Understanding and Implementing RouterOS
Study material for the MTCNA Certification Course, updated to RouterOS v7
In RouterOS, a PPPoE disconnection that is signaled as a “peer request” typically occurs when the peer (that is, the other end of the PPPoE connection, which is typically the ISP's PPPoE server) requests to terminate the session.
At the end of the article you will find a small test that will allow you assess the knowledge acquired in this reading
This may be due to several reasons, including:
If there is a problem with the login credentials (username and password), the server may terminate the session.
The PPPoE server may have policies to disconnect sessions after a certain time or due to usage restrictions.
Incorrect configurations on the client or server side can lead to disconnections. This may include timeout settings, MTU, or issues with PPPoE session negotiation.
The server could be undergoing maintenance or have technical issues causing disconnections.
Physical line problems or interference can cause disconnections. This can be especially common on DSL connections.
To diagnose and resolve this issue, you can try the following steps:
If the problem persists after these steps, it may be helpful to perform additional tests, such as changing the hardware or testing the connection in a different environment, to rule out possible causes.
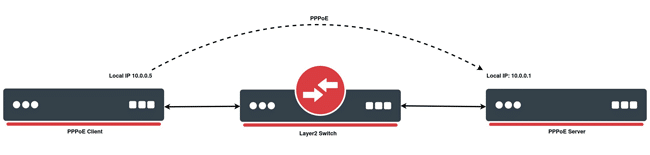
On a PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) connection, the recommended values for the MRU (Maximum Receive Unit) and MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) may vary depending on the specific environment and the requirements of the Internet service provider.
However, there are some general practices you can follow:
It is important to remember that incorrect MRU and MTU values can lead to problems such as packet fragmentation, packet loss, or an overall decrease in network efficiency, so making careful adjustments and extensive testing is crucial.
This example assumes that you already have a PPPoE client interface configured and that you only need to adjust these parameters:
/interface pppoe-client
set [find] add-default-route=yes use-peer-dns=yes \
mru=1492 mtu=1492 name=pppoe-out1 \
user="your_user" password="your_password"
/ip firewall mangle
add action=change-mss chain=forward new-mss=1452 \
protocol=tcp tcp-flags=syn out-interface=pppoe-out1 passthrough=yes
add action=change-mss chain=forward new-mss=1452 \
protocol=tcp tcp-flags=syn in-interface=pppoe-out1 passthrough=yes
Find the existing PPPoE client interface and apply the following settings.
Add rules to the firewall mangle table to adjust the MSS of TCP packets with the SYN flag, to ensure that they do not exceed the maximum effective size allowed after PPPoE encapsulation.
This is just a basic example. You will need to adjust the interface names, user and password values, and any other parameters specific to your network and requirements.
Also, it is important to test these changes in a controlled environment to ensure that they do not interrupt your Internet connection.
Study material for the MTCNA Certification Course, updated to RouterOS v7
Study material for the MTCNA Certification Course, updated to RouterOS v7
Av. Juan T. Marengo and J. Orrantia
Professional Center Building, Office 507
Guayaquil. Ecuador
Zip Code 090505
to our weekly newsletters
Copyright © 2024 abcxperts.com – All Rights Reserved
Take advantage of the Three Kings Day discount code!
Take advantage of the New Year's Eve discount code!
Take advantage of the discount code for Christmas!!!
all MikroTik OnLine courses
all Academy courses
all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
Take advantage of the discount codes for Cyber Week!!!
all MikroTik OnLine courses
all Academy courses
all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
Take advantage of the discount codes for Black Friday!!!
**Codes are applied in the shopping cart
Take advantage of discount codes for Halloween.
Codes are applied in the shopping cart
11% discount on all MikroTik OnLine courses
11%
30% discount on all Academy courses
30%
25% discount on all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
25%