RouterOS v7 Advanced Routing Book
Study material for the MTCRE Certification Course, updated to RouterOS v7
In network environments, the availability and reliability of services are essential to ensure uninterrupted operation. Router redundancy protocols play a crucial role in providing mechanisms that enable service continuity in the event of network device failures.
At the end of the article you will find a small test that will allow you assess the knowledge acquired in this reading
Three of the most used protocols to achieve this redundancy are HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol), VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) and GLBP (Gateway Load Balancing Protocol).
El Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a router redundancy protocol developed by Cisco. Its primary purpose is to provide high availability and redundancy for IP networks, ensuring continuous operation in the event of a router failure.
HSRP allows multiple routers to work together as a group to provide a single virtual access point (gateway).
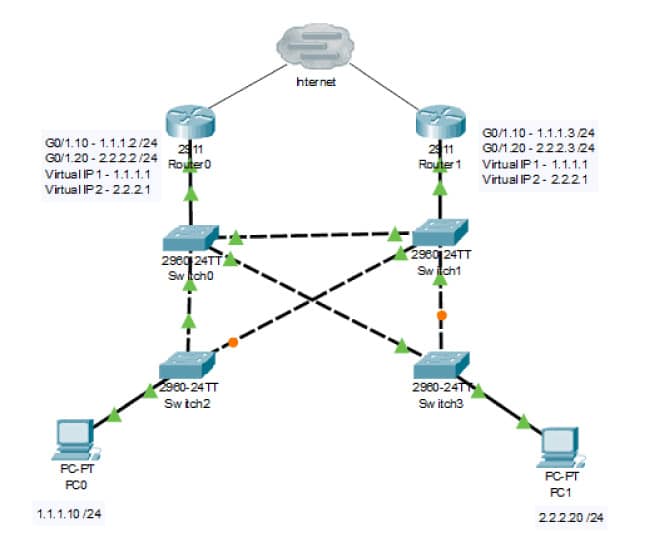
Key aspects about HSRP:
HSRP is a commonly used solution to ensure redundancy at the network access layer, especially in enterprise environments where service continuity is critical.
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) is another router redundancy protocol designed to provide high availability and reliability in IP networks. Like HSRP, VRRP allows multiple routers to work together as a group to form a virtual gateway.
However, VRRP is an IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) standard, which means it is not limited to Cisco devices and is interoperable between different network equipment manufacturers.
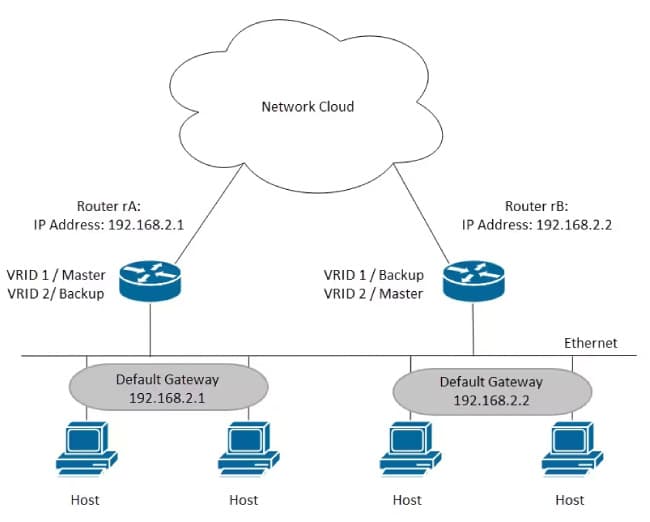
Key points about VRRP:
VRRP is a common option to provide redundancy in heterogeneous environments where devices from different manufacturers are used.
Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) is another router redundancy protocol developed by Cisco, but unlike HSRP and VRRP, GLBP goes beyond simply providing redundancy by distributing the traffic load across multiple routers.
This protocol is designed to optimize network resource utilization and improve performance by effectively balancing load.
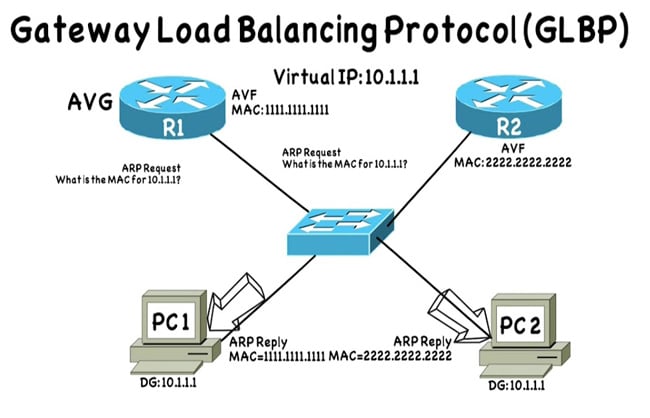
Important facts about GLBP:
GLBP is especially useful in environments where you want to take full advantage of the capacity of multiple routers and distribute the load evenly to improve network performance.
This table provides a general comparison of the key features of HSRP, VRRP, and GLBP. Choosing between these protocols will depend on your specific network requirements, interoperability with other network devices, and the need for additional features such as load balancing.
Feature | HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) | VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) | GLBP (Gateway Load Balancing Protocol) |
Developer | Cisco | IETF (Open Standard) | Cisco |
Standard Protocol | Owners | IETF standard | Owners |
Cross-platform Compatibility | Limited (Mainly Cisco) | Broad (IETF Standard) | Limited (Mainly Cisco) |
Load Distribution | No | No | Yes |
Load balance | No | No | Yes |
Multiple Router Support | No | Yes | Yes |
Number of Groups | 16 | 255 | 1024 (per interface) |
Priority for Election | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Tiebreaker with IP Address | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Virtual Groups by Interface | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Routing Protocol | Does not depend on the routing protocol | Does not depend on the routing protocol | Does not depend on the routing protocol |
IPv6 support | Yes (depends on platform and software version) | Yes (depends on platform and software version) | Yes (depends on platform and software version) |
Active Simultaneous Connections | 1 (per group) | 1 (per group) | Multiple (load ratio) |
Load balancing | No | No | Yes (based on loading algorithm) |
Implementation Standard | RFC 2281 | RFC 5798 | Non-standard (proprietary implementation) |
Mainly used in | Cisco networks | Heterogeneous networks, mixed environments | Cisco networks |
In the networking space, router redundancy protocols such as HSRP, VRRP, and GLBP play a crucial role in ensuring the availability and reliability of services. HSRP, developed by Cisco, lays the foundation by allowing multiple routers to work as a group, ensuring a smooth transition between active and standby devices in the event of failures.
VRRP, an IETF standard, shares similar goals but promotes interoperability between devices from different manufacturers. For its part, GLBP, also from Cisco, goes further by not only providing redundancy, but also balancing the traffic load between active routers, thus improving network efficiency.
The choice between these protocols will depend on the specific infrastructure and particular requirements of each network.
Study material for the MTCRE Certification Course, updated to RouterOS v7
Av. Juan T. Marengo and J. Orrantia
Professional Center Building, Office 507
Guayaquil. Ecuador
Zip Code 090505
to our weekly newsletters
Copyright © 2024 abcxperts.com – All Rights Reserved
40% discount on MikroTik books and book packs - Discount Code: AN24-LIB Discard
Take advantage of the Three Kings Day discount code!
Take advantage of the New Year's Eve discount code!
Take advantage of the discount code for Christmas!!!
all MikroTik OnLine courses
all Academy courses
all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
Take advantage of the discount codes for Cyber Week!!!
all MikroTik OnLine courses
all Academy courses
all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
Take advantage of the discount codes for Black Friday!!!
**Codes are applied in the shopping cart
Take advantage of discount codes for Halloween.
Codes are applied in the shopping cart
11% discount on all MikroTik OnLine courses
11%
30% discount on all Academy courses
30%
25% discount on all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
25%