Advanced Traffic Control Book, RouterOS v7
Study material for the MTCTCE Certification Course, updated to RouterOS v7
MikroTik provides firewall functionality that includes both Stateful rules and Stateless rules. The firewall implements stateful (through connection tracking) and stateless packet filtering and therefore provides security functions that are used to manage the flow of data to, from, and through the router.
Along with Network Address Translation (NAT), it serves as a tool to prevent unauthorized access to directly connected networks and to the router itself, as well as a filter for outgoing traffic.
At the end of the article you will find a small test that will allow you assess the knowledge acquired in this reading
These rules follow the state of connections, meaning that the firewall keeps track of the state of each connection and allows traffic based on the connection state. This is useful for allowing response traffic on connections initiated from within the network.
This allows them to make more informed decisions about which packets to allow or block, depending on the context of the connection. For example, a stateful firewall would allow a response packet to pass through a previously allowed request packet, even if the request packet itself is not explicitly included in the firewall rules.
Stateful offers enhanced security benefits as it can effectively prevent unauthorized access attempts and protect against phishing attacks.
They also provide better application-level filtering capabilities, allowing you to control which applications and protocols can communicate through the firewall.
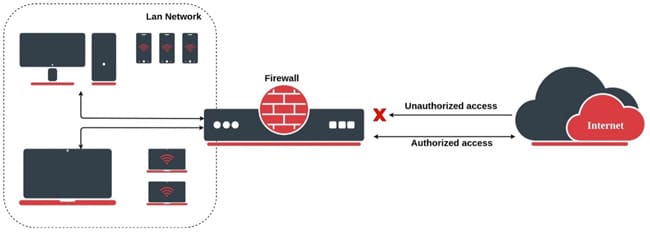
These rules do not follow the state of connections and are applied independently to each packet. Each packet is filtered according to the criteria established by the rule, regardless of previous connections.
Stateless on the other hand, do not maintain a state table and only inspect individual packets based on their source and destination addresses, ports, and protocol headers.
They operate as packet filters, making decisions based solely on the information contained in each packet.
Feature | stateful firewall | Stateless Firewall |
Connection tracking
| Si | No |
Security
| Improved | Basic |
Application level filtering
| Granular | Limited |
Performance
| Lower | Higher |
Consumption of resources
| Higher | Lower |
Suitability
| Enterprise networks, sensitive applications | Home networks, high bandwidth environments |
In MikroTik RouterOS, stateless firewall rules are created without taking into account the state of the connections, that is, they are applied regardless of previous connections. Here are some examples of stateless rules that could be useful in certain scenarios:
/ip firewall filter add chain=forward src-address=192.168.1.100 action=accept
This rule allows traffic coming from the IP address 192.168.1.100 in the forwarding chain.
/ip firewall filter add chain=forward src-address=192.168.2.0/24 action=accept
This rule allows traffic from the 192.168.2.0/24 subnet in the forwarding chain.
/ip firewall filter add chain=forward dst-address=203.0.113.10 action=drop
This rule blocks all traffic going to the IP address 203.0.113.10 in the forwarding chain.
These are just examples and you should adapt the rules based on your specific needs and your network topology. Also, keep in mind that these rules are stateless, so they do not take into account the state of previous connections.
In MikroTik RouterOS, stateful firewall rules focus on the state of connections, meaning they allow or block traffic based on the connection state. Here are some examples of stateful rules:
/ip firewall filter add chain=forward connection-state=established,related action=accept
This rule allows traffic that is part of an established or related connection in the forwarding chain.
/ip firewall filter add chain=forward in-interface=ether1 connection-state=new protocol=tcp dst-port=80 action=accept
This rule allows TCP traffic destined for port 80 from the outside through the ether1 interface in the forwarding chain.
/ip firewall filter add chain=input connection-state=new action=drop
This rule blocks all incoming traffic that is not part of an established connection in the incoming chain.
/ip firewall filter add chain=input connection-state=new protocol=icmp action=accept
This rule allows incoming ICMP traffic for ping requests in the inbound chain.
/ip firewall filter add chain=input in-interface=ether1 connection-state=new dst-port=22 action=drop
This rule blocks incoming traffic to port 22 (SSH) from the outside through the ether1 interface in the inbound chain.
These are just examples and you should adjust the rules based on your specific requirements and network configuration. Stateful rules are essential to allow necessary traffic and maintain security by blocking unwanted traffic.
Study material for the MTCTCE Certification Course, updated to RouterOS v7
Av. Juan T. Marengo and J. Orrantia
Professional Center Building, Office 507
Guayaquil. Ecuador
Zip Code 090505
to our weekly newsletters
Copyright © 2024 abcxperts.com – All Rights Reserved
40% discount on MikroTik books and book packs - Discount Code: AN24-LIB Discard
Take advantage of the Three Kings Day discount code!
Take advantage of the New Year's Eve discount code!
Take advantage of the discount code for Christmas!!!
all MikroTik OnLine courses
all Academy courses
all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
Take advantage of the discount codes for Cyber Week!!!
all MikroTik OnLine courses
all Academy courses
all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
Take advantage of the discount codes for Black Friday!!!
**Codes are applied in the shopping cart
Take advantage of discount codes for Halloween.
Codes are applied in the shopping cart
11% discount on all MikroTik OnLine courses
11%
30% discount on all Academy courses
30%
25% discount on all MikroTik Books and Book Packs
25%